Create a healthier and brighter future
Neumina™ is more than a brand;
it represents a lifestyle that combines nature and science
to promote physical and mental well-being.
Neumina™ is the result of deep exploration
of nature's mysteries and a relentless pursuit of scientific innovation.
Our brand's spirit is profoundly based in respect for nature.

Neumina™ is more than a brand;
it represents a lifestyle that combines nature and science
to promote physical and mental well-being.

Rhodiola Rosea is an adaptogen herb primarily found in Tibet, China, with a documented usage history spanning over 5,000 years. Modern scientific research has revealed that Rhodiola Rosea exhibits various pharmacological effects, including resistance to hypoxia and fatigue, protection of cardiac and pulmonary functions, stabilization of blood oxygen levels, and enhancement of athletic performance. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) plays a critical role in mitigating hypoxic responses at high altitudes[1].
Studies have demonstrated that salidroside, an active compound in Rhodiola rosea, can promote the expression of HIF-1 under hypoxic conditions, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways and alleviating hypoxia-induced damage to the body[2].
Furthermore, Rhodiola Rosea protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced cellular damage by participating in mitochondrial processes such as acetyl-CoA synthesis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle[3]. Animal experiments and clinical trials indicate that salidroside enhances endurance and strength-related athletic performance[4]. It improves exercise speed and accuracy, reduces mental fatigue, and accelerates reaction times[5].
Additionally, it alleviates muscle damage and inflammation caused by exercise, mitigates energy system exhaustion, and counters oxidative stress responses[6]. Salidroside increases blood oxygen saturation in hypoxic conditions, decreases arterial hemoglobin content, and restores blood PH to within the normal range, thereby improving cardiopulmonary function and alleviating hypoxemia[4].
Moreover, salidroside aids in restoring normal alveolar cell functions. It reduces oxidative free radicals, such as malondialdehyde and interleukins, while increasing antioxidant components like glutathione and superoxide dismutase, thus protecting the body from oxidative stress-induced damage[7].
References
[1] Webb JD, Coleman ML, Pugh CW. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF), HIF hydroxylases and oxygen sensing. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(22):3539–3554.
[2] Yan X, et al. Salidroside orchestrates metabolic reprogramming by regulating the Hif1α signalling pathway in acute mountain sickness. Pharm Biol. 2021;59(1):1540–1550.
[3] Zhang X, Xie L, Long J, Xie Q, Zheng Y, Liu K, Li X. Salidroside: A review of its recent advances in synthetic pathways and pharmacological properties. Chem Biol Interact. 2021 Apr 25;339:109268.
[4] Tinsley GM, et al. Rhodiola rosea as an adaptogen to enhance exercise performance: a review of the literature. Br J Nutr. 2024;131(3):461–473.
[5] Spasov AA, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of the stimulating and adaptogenic effect of Rhodiola rosea SHR-5 extract on the fatigue of students caused by stress during an examination period with a repeated low-dose regimen. Phytomedicine. 2000;7(2):85–89.
[6] Jówko E, et al. Effects of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on mental performance, physical capacity, and oxidative stress biomarkers in healthy men. J Sport Health Sci. 2018;7(4):473–480.
[7] Wang Z, et al. Protective effect of salidroside on lung tissue in rats exposed rapidly to high altitude. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022;51(4):422–429.
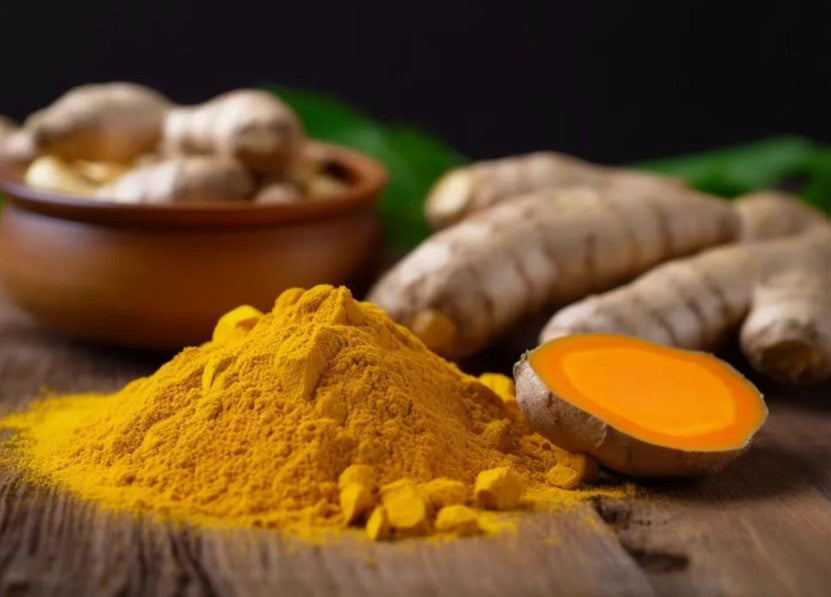

A meta-analysis encompassing 15 randomized controlled trials with a total of 1,621 participants demonstrated that for patients with osteoarthritis (OA), turmeric extract and curcumin could alleviate joint pain and stiffness while improving joint function compared to placebo. However, a noticeable effect required more than 12 weeks of treatment. In these trials, the daily doses of turmeric extract or curcumin ranged from 40 mg to 1,000 mg, with no significant adverse reactions reported[2].
Another meta-analysis involving 29 randomized controlled trials with a total of 2,396 arthritis patients (including ankylosing spondylitis [AS], rheumatoid arthritis [RA], osteoarthritis [OA], juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and gout/hyperuricemia-induced arthritis) revealed that daily supplementation with 40–2,000 mg of turmeric extract or curcumin over 4–36 weeks generally mitigated inflammation severity and pain levels in these patients, with excellent safety profiles[3].
A third meta-analysis comprising 16 randomized controlled trials involving 1,028 participants indicated that curcumin supplementation positively influenced liver ultrasound results, serum liver enzymes, and serum total cholesterol levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). These findings suggest that curcumin may serve as a reasonable adjunctive therapy for NAFLD patients[4].
Additionally, a meta-analysis based on 7 randomized controlled trials with 447 participants suggested that curcumin supplementation beneficially affected serum markers of inflammation and glycolipid metabolism in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)[5].
However, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) revised its guidelines on September 25, 2018, cautioning that individuals with bile duct obstruction, cholangitis, liver disease, gallstones, or other biliary tract disorders should avoid curcumin supplements due to potential risks[1].
References
[1] European Medicines Agency. European Union Herbal Monograph on Curcuma Longa L., Rhizoma Final. Comm. Herb. Med. Prod. 2018;44:1–7.
[2] Zeng L, Yu G, Hao W, Yang K, Chen H. The efficacy and safety of Curcuma longa extract and curcumin supplements on osteoarthritis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Biosci Rep. 2021 Jun 25;41(6):BSR20210817.
[3] Zeng L, Yang T, Yang K, Yu G, Li J, Xiang W, Chen H. Efficacy and Safety of Curcumin and Curcuma longa Extract in the Treatment of Arthritis: A Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis of Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:891822.
[4] Ngu MH, Norhayati MN, Rosnani Z, Zulkifli MM. Curcumin as adjuvant treatment in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) disease: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Complement Ther Med. 2022 Sep;68:102843.
[5] Shen W, Qu Y, Jiang H, Wang H, Pan Y, Zhang Y, Wu X, Han Y, Zhang Y. Therapeutic effect and safety of curcumin in women with PCOS: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 27;13:1051111.

Ashwagandha is a traditional medicinal plant originated from South Africa and is also an adaptogen herb, also known as Kanna or Channa. Ashwagandha is mainly extracted from the above-ground part of a succulent plant, which is widely distributed in the arid regions of South Africa. Local indigenous people, such as the Koisan people, have been using Ashwagandha for thousands of years as a natural mood regulator and a herb for treating various diseases.
Modern research shows that Ashwagandha demonstrates potential in anti-depression, anti-anxiety and mood improvement, and is also helpful in relieving stress, improving sleep quality, enhancing memory and concentration. The main active ingredients of Ashwagandha are alkaloid compounds, especially mesembrine, which have a significant effect on the nervous system. Modern research shows that Ashwagandha can increase the level of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the brain, which is a neurotransmitter closely related to mood, anxiety and well-being[1].
Ashwagandha can significantly reduce stress and anxiety while lowering cortisol levels, with mild side effects. It is a promising natural mood regulator supplement[2].Daily supplementation of 500 mg of Ashwagandha extract can significantly reduce stress and anxiety, improve quality of life and cognitive function in people with mild to moderate anxiety and stress. Its mechanism of action includes reducing cortisol and increasing serotonin levels, and it has good safety[3]. The analysis included 12 eligible papers with a total sample size of 1,002 participants, aged between 25 and 48. Supplementation with Ashwagandha can significantly reduce anxiety and stress levels. Current systematic reviews and dose-response meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials show that supplementation with Ashwagandha has beneficial effects on both stress and anxiety[4].
Five randomized controlled trials were analyzed, involving a total of 400 subjects. Ashwagandha extract has a beneficial effect on improving sleep in adults. This is particularly prominent among adults diagnosed with insomnia, with a therapeutic dose of ≥600 mg/day and a treatment duration of ≥8 weeks[5].
References
[1] Swart AC, Smith C. Modulation of glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid and androgen production in H295 cells by Trimesemine™, a mesembrine-rich Sceletium extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2016;177:35-45.
[2] Arumugam V, Vijayakumar V, Balakrishnan A, B Bhandari R, Boopalan D, Ponnurangam R, Sankaralingam Thirupathy V, Kuppusamy M. Effects of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on stress and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EXPLORE. 2024;20(6):103062. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2024.103062
[3] Majeed M, Nagabhushanam K, Mundkur L. A standardized Ashwagandha root extract alleviates stress, anxiety, and improves quality of life in healthy adults by modulating stress hormones: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Medicine. 2023;102(41):e35521. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000035521
[4] Akhgarjand C, Asoudeh F, Bagheri A, Kalantar Z, Vahabi Z, Shab-Bidar S, Rezvani H, Djafarian K. Does Ashwagandha supplementation have a beneficial effect on the management of anxiety and stress? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother Res. 2022 Nov;36(11):4115-4124. doi:10.1002/ptr.7598. Epub 2022 Aug 25. PMID: 36017529.
[5] Cheah KL, Norhayati MN, Husniati Yaacob L, Abdul Rahman R. Effect of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) extract on sleep: A systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS One. 2021 Sep 24;16(9):e0257843. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0257843. PMID: 34559859; PMCID: PMC8462692.
[6] Fry CH, Fluck D, Han TS. Adrenal hypofunction associated with ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) supplementation: a case report. Toxicol Environ Health Sci. 2022;14:141–145. doi:10.1007/s13530-022-00122-z
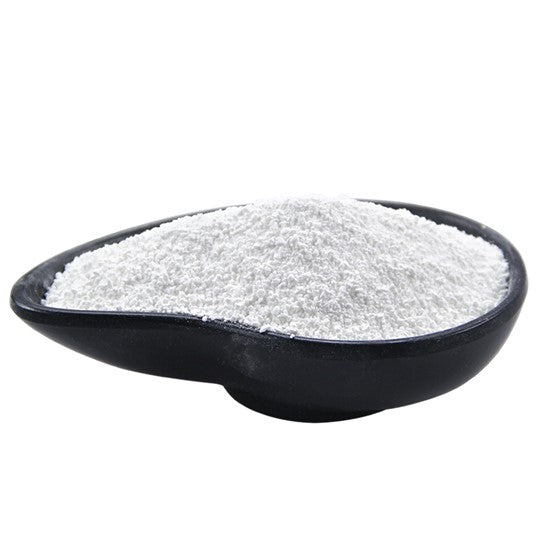

Magnesium is one of the essential trace elements for the human body. It plays a critical role not only in muscle contraction, nerve function, and bone health but also in facilitating hundreds of enzymatic reactions that influence the metabolic processes of nearly every cell. Therefore, maintaining an adequate level of magnesium intake is vital for overall bodily health[1].
In the nervous system, magnesium is involved in the transmission of neural signals between neurons and the regulation of muscle responses. It inhibits excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate, thereby protecting nerve cells. By regulating calcium ion influx into neurons, it helps suppress neuroinflammation and reduce oxidative stress. Clinical studies have demonstrated that magnesium has a certain alleviating effect on anxiety symptoms[2].
A study involving 3,964 participants assessed sleep quality and dietary magnesium or magnesium supplement intake, adjusting for potential confounding factors. The results indicated a significant correlation between magnesium intake and improved sleep quality. Among individuals without depressive disorders, those in the highest magnesium intake group were less likely to experience less than 7 hours of sleep and exhibited better sleep quality. In contrast, among individuals with depressive disorders, no significant relationship was observed between sleep quality and magnesium intake. However, within the higher magnesium intake group, depressive symptoms were found to be reduced[3].
Different magnesium compound supplements exhibit distinct characteristics: Magnesium glycinate can soothe the nerves and help to fall asleep. Magnesium malate can relieve cramps and improve athletic performance. Magnesium citrate can promote digestion and has a better absorption effect. Triple compound magnesium supplement, avoiding the insufficiency of the effect of a single ingredient.[4].
References
[1] Al Alawi AM, Majoni SW, Falhammar H. Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions. Int J Endocrinol. 2018 Apr 16;2018:9041694. doi:10.1155/2018/9041694. PMID: 29849626; PMCID: PMC5926493.
[2] Kirkland AE, Sarlo GL, Holton KF. The Role of Magnesium in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients. 2018;10(6):730. doi:10.3390/nu10060730
[3] Zhang Y, Chen C, Lu L, Knutson KL, Carnethon MR, Fly AD, Luo J, Haas DM, Shikany JM, Kahe K. Association of magnesium intake with sleep duration and sleep quality: findings from the CARDIA study. Sleep. 2022 Apr 11;45(4):zsab276. doi:10.1093/sleep/zsab276. PMID: 34883514; PMCID: PMC8996025.
[4] Blaquiere C, Berthon G. Speciation studies in relation to magnesium bioavailability: formation of Mg(II) complexes with glutamate, aspartate, glycinate, lactate, pyroglutamate, pyridoxine and citrate, and appraisal of their potential significance towards magnesium gastrointestinal absorption. Inorganica Chimica Acta. 1987;135(3):179–189. doi:10.1016/s0020-1693(00)81296-7
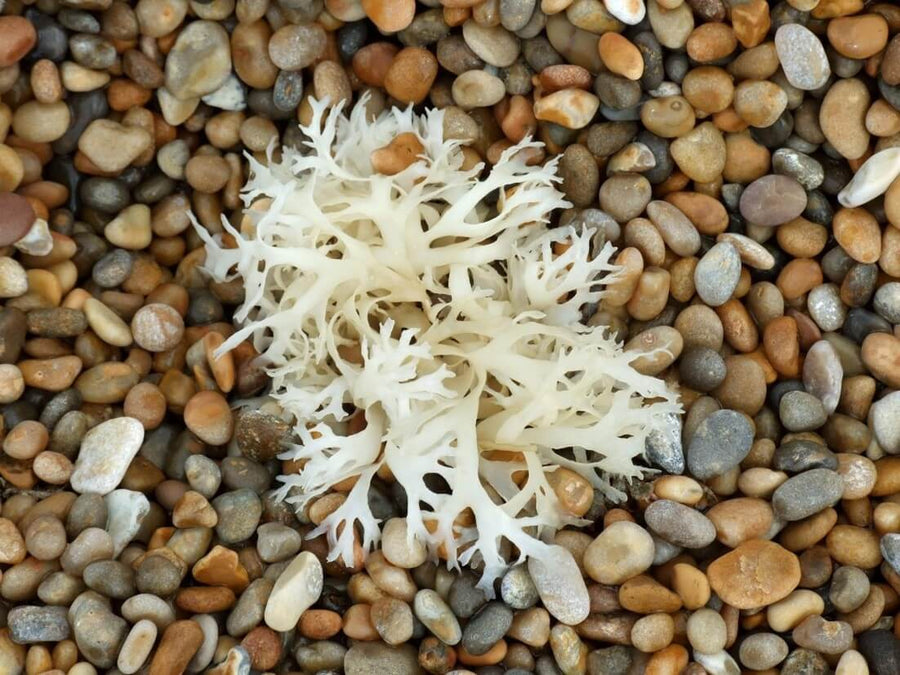

Sea Moss is rich in vitamins, minerals, and other bioactive compounds that contribute to its many health-supporting benefits. Its nutrient-dense profile makes it a valuable addition to a balanced diet and a powerful ally in supporting various aspects of health, from immune function to hormonal balance. The immune-boosting properties of Sea Moss make it a valuable addition to your wellness routine. The diverse array of bioactive nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and polysaccharides, contributes to its ability to fortify the body's defenses against infections and illnesses[2].
The unique combination of nutrients, including polyphenols, flavonoids, and sulfated polysaccharides like carrageenan, may help promote a healthy immune response[3]. This promotes a balanced and effective defense against unwanted organisms and compounds. The natural detoxifying agents present in sea moss, such as alginates, help remove heavy metals and other toxins from the body[1].
By binding to these harmful substances, Sea Moss aids in their elimination, promoting a healthy and well-functioning system. This detoxification process is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing the accumulation of toxins that could lead to various health issues. The carrageenan in Sea Moss, acting as a prebiotic, may promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria[4].
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for efficient digestion and nutrient absorption, further supporting the body's detoxification processes. Sea Moss has been shown to support heart health by promoting healthy circulation, supporting a healthy inflammatory response, and encouraging healthy cholesterol levels[5].
Hormonal balance is crucial for overall health, and Sea Moss plays a supportive role in this aspect. The iodine content in sea moss is particularly noteworthy, as it influences thyroid function—impacting the production and regulation of hormones throughout the body[6].
Reference
[1] Lomartire S, Marques JC, Gonçalves AM. An overview to the health benefits of seaweeds consumption. Marine Drugs. 2021;19(6):341.
[2] Palstra AP, Kals J, Blanco Garcia A, Dirks RP, Poelman M. Immunomodulatory effects of dietary seaweeds in LPS challenged Atlantic salmon Salmo salar as determined by deep RNA sequencing of the head kidney transcriptome. Frontiers in Physiology. 2018;9:625.
[3] Liu J, Kandasamy S, Zhang J, Kirby CW, Karakach T, Hafting J, et al. Prebiotic effects of diet supplemented with the cultivated red seaweed Chondrus crispus or with fructooligo-saccharide on host immunity, colonic microbiota and gut microbial metabolites. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2015;15:1-12.
[4] Lopez-Santamarina A, Miranda JM, Mondragon ADC, Lamas A, Cardelle-Cobas A, Franco CM, Cepeda A. Potential use of marine seaweeds as prebiotics: A review. Molecules. 2020;25(4):1004.
[5] Taboada C, Millán R, Míguez I. Composition, nutritional aspects and effect on serum parameters of marine algae Ulva rigida. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2010;90(3):445-449.
[6] Combet E, Ma ZF, Cousins F, Thompson B, Lean ME. Low-level seaweed supplementation improves iodine status in iodine-insufficient women. British Journal of Nutrition. 2014;112(5):753-761.
NAD+, a pivotal coenzyme, plays an essential role incellular energy metabolism, DNA damage repair, and mitochondrial function modulation. NAD+ is the "central molecule" of cellular energy metabolism and anti-aging regulation. Maintaining its stable level is crucial for healthy aging.[2] With NAD+ supplement, the aging rate of stem cells decreased to about 40% of normal levels.[1]
NAD+ is not only the hub of energy metabolism, but also plays the role of a key signaling factor connecting environmental sensing, cell fate regulation and disease progression.[3]With the inevitable decline in NAD+ as you age, your energy production and cellular repair also decline. This reduction leads to energy loss, mental fatigue, wrinkles, and frequent sickness. Though there's no way to stop this from happening, you can fill in the gaps with NAD+ supplementation.
Research on people with chronic fatigue syndrome evaluated the safety and effectiveness of NAD+ supplementation on fatigue, quality of life, and sleep quality. The overall consensus is that supplementing with NAD+ has a positive effect on quality of life and improves health parameters like anxiety, energy, and immune system response.[4]Because NAD+ is involved in mechanisms of DNA repair that help protect cells from damage caused by stress, oxidative damage, and aging, higher levels (as a result of supplementation) may promote a more efficient process. One study investigated the role of NAD+ supplementation on DNA repair. Researchers found that supplementation decreased the accumulation of endogenous DNA damage and improved DNA repair capacity.
Ultimately, supplementing with NAD+ may positively impact DNA repair in the context of aging and in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's disease.[5]Take it daily to help the body achieve a higher NAD+ baseline, leading to lasting supports healthy aging, boosts cellular energy, supports immune function, promotes skin and hair vitality.
Reference
[1] Zheng z, wang X, 0uyang L, chen w, zhang l,cao y, Antioxidants lmorove the prolferation and ficacy of huc-Mscs against H202-Induced senescence. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 24;12(7):1334.doi: 10.3390/antiox12071334. PMID: 37507874; PMCID: PMC10376626.
[2] Covarrubias, A. J., Perrone, R., Grozio, A., & Verdin, E. (2021). NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 22(2), 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00313-x
[3] Xie, N., Zhang, L., Gao, W. et al. NAD+ metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Sig Transduct Target Ther 5, 227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00311-7
[4] Gindri IM, Ferrari G, Pinto LPS, Bicca J, Dos Santos IK, Dallacosta D, Roesler CRM. Evaluation of safety and effectiveness of NAD in different clinical conditions: a systematic review. AmJ Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Apr 1;326(4):E417-E427. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00242.2023
[5] Wilk A, Hayat F, Cunningham R, Li J, Garavaglia S, Zamani L, Ferraris DM, Sykora P, Andrews J, Clark J, Davis A, Chaloin L, Rizzi M, Migaud M, Sobol RW. Extracellular NAD+ enhances PARP-dependent DNA repair capacity independently of CD73 activity. Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 20;10(1):651. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-57506-9

Cordyceps is a type of fungus long used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)[1]. It is said to have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, with potential health benefits for improved heart health and may support healthy glucose metabolism already within the normal range[2].
In complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), cordyceps is often used as a natural energy booster. One study found that daily supplement use gradually increased the maximum oxygen intake (VO2 max) in young adults after three weeks. Researchers believed the results meant that cordyceps might increase an athlete's tolerance to high-intensity exercise[3].
Cordyceps is believed to have potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which may help prevent or treat hyperlipidemia. Results from animal studies linked cordyceps use to lowered hyperlipidemia. In one such study, a polysaccharide extracted from cordyceps decreased hamsters' total cholesterol and triglyceride levels[4]. Cordyceps has been shown to stimulate the immune system by increasing the activity and production of various immune cells. A 2023 study concluded that cordyceps can be a safe and effective treatment to enhance care in patients with mild to moderate COVID19 infection[5].
In older research, a 2015 randomized controlled trial demonstrated that healthy adult males taking 1.5 grams of cordyceps daily for four weeks effectively enhanced their cellular immunity (the destruction of infected cells or pathogens)[6].
The aging process of tissues and organs is a natural process accompanied by a gradual weakening of the body. Research published in 2022 concluded that mushrooms, including cordyceps, may limit some naturally occurring changes due to age, such as hypertension and memory decline[7].
Reference
[1] Peng T, Guo J, Tong X. Advances in biosynthesis and metabolic engineering strategies of cordycepin. Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 5;15:1386855. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2024
[2] Ashraf SA, Elkhalifa AEO, Siddiqui AJ, et al. Cordycepin for health and wellbeing: A potent bioactive metabolite of an entomopathogenic cordyceps medicinal fungus and its nutraceutical and therapeutic doi:10.3390/molecules25122735 potential. Molecules. 2020;25(12):2735.
[3] Hirsch KR, Smith-Ryan AE, Roelofs EJ, et al. Cordyceps militaris improves tolerance to high-intensity exercise after acute and chronic supplementation. J Diet Suppl. 2017;14(1):42-53. doi:10.1080/19390211.2016.1203386
[4] Yu WQ, Yin F, Shen N, et al. Polysaccharide CM1 from cordyceps militaris hinders adipocyte differentiation and alleviates hyperlipidemia in LDLR(+/-) hamsters. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1):178. doi:10.1186/s12944-021-01606-6
[5] Dubhashi S, Sinha S, Dwivedi S, et al. Early trends to show the efficacy of cordyceps militaris in mild to moderate COVID inflammation. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e43731. doi:10.7759/cureus.43731
[6] Kang HJ, Baik HW, Kim SJ, et al. Cordyceps militaris enhances cell-mediated immunity in healthy Korean men. J Med Food. 2015;18(10):1164-1172. doi:10.1089/jmf.2014.3350
[7] Bhambri A, Srivastava M, Mahale VG, Mahale S, Karn SK. Mushrooms as potential sources of active metabolites and medicines. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:837266. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.837266

Lion’s mane mushrooms, also known as Hericium erinaceus, hou tou gu or yamabushitake, have both culinary and medicinal uses in Asian countries like China, India, Japan, and Korea[1]. Studies have found that lion’s mane mushrooms contain two special compounds that can stimulate the growth of brain cells: hericenones and erinacines[2].
Additionally, animal studies have found that lion’s mane may help protect against Alzheimer’s disease. In fact, lion’s mane mushroom and its extracts have been shown to reduce symptoms of memory loss in mice, as well as prevent neuronal damage caused by amyloid-beta plaques, which accumulate in the brain during Alzheimer’s disease[3].
A 2020 study of people with mild Alzheimer’s disease found that supplementation with 1 gram of lion’s mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks significantly improved cognitive test scores compared with a placebo[4]. Research shows that lion’s mane mushrooms contain powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds that may help reduce the impact of these illnesses. Animal research has found that lion’s mane mushroom extract has anti-inflammatory effects that can reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression in mice[5].
Other animal studies have found that lion’s mane extract can also help regenerate brain cells and improve the functioning of the hippocampus, a region of the brain that processes memories and emotional responses[6]. A strong immune system protects the body from bacteria, viruses, and other disease causing pathogens.
Animal research shows that lion’s mane mushroom can boost immunity by increasing the activity of the intestinal immune system, which protects the body from pathogens that enter the gut through the mouth or nose[7].
Reference
[1] Friedman M. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health-Promoting Properties of Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane) Mushroom Fruiting Bodies and Mycelia and Their Bioactive Compounds. J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Aug doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02914. Epub 2015 Aug 5. PMID: 26244378. 19;63(32):7108-23.
[2] Kushairi N, Phan CW, Sabaratnam V, David P, Naidu M. Lion's Mane Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. Suppresses H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage and LPS-Induced Inflammation in HT22 Hippocampal Neurons and BV2 Microglia. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 1;8(8):261. doi:10.3390/antiox8080261. PMID: 31374912; PMCID: PMC6720269.
[3] Tsai-Teng T, Chin-Chu C, Li-Ya L, Wan-Ping C, Chung-Kuang L, Chien-Chang S, ChiYing HF, Chien-Chih C, Shiao YJ. Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelium ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-related pathologies in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice. J Biomed Sci. 2016 Jun 27;23(1):49. doi:10.1186/s12929-016-0266-z. PMID: 27350344; PMCID: PMC4924315.
[4] Li IC, Chang HH, Lin CH, Chen WP, Lu TH, Lee LY, Chen YW, Chen YP, Chen CC, Lin DP. Prevention of Early Alzheimer's Disease by Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus Mycelia Pilot Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jun 3;12:155. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2020.00155. PMID: 32581767; PMCID: PMC7283924.
[5] Chiu CH, Chyau CC, Chen CC, Lee LY, Chen WP, Liu JL, Lin WH, Mong MC. Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus Mycelium Produces Antidepressant-Like Effects through Modulating BDNF/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Signaling in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 24;19(2):341. doi:10.3390/ijms19020341. PMID: 29364170; PMCID: PMC5855563.
[6] Ryu S, Kim HG, Kim JY, Kim SY, Cho KO. Hericium erinaceus Extract Reduces Anxiety and Depressive Behaviors by Promoting Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Brain. J Med Food. 2018 Feb;21(2):174-180. doi:10.1089/jmf.2017.4006. Epub 2017 Nov 1. PMID: 29091526.
[7] Sheng X, Yan J, Meng Y, Kang Y, Han Z, Tai G, Zhou Y, Cheng H. Immunomodulatory effects of Hericium erinaceus derived polysaccharides are mediated by intestinal immunology. Food Funct. 2017 Mar 22;8(3):1020-1027. doi:10.1039/c7fo00071e. PMID: 28266682.

Limited Time
Testimonials
